Normal Size of Ovary
-by Abhrajita Mondal
–Reading Time – 14 min Approx
Are you curious about the normal size of ovary? Before you jump to conclusions, let us throw some light on the female reproductive system.
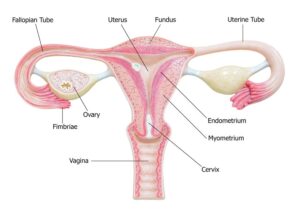 The organs in the female reproductive system help to sustain the female sex cells and secrete female hormones. It helps in the transportation of the cells to the site of fertilization and also lodges the fertilized egg cell on the wall of the uterus. It carries out a complicated process. The female reproductive system consists of the vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, external genital organs, and the uterus.
The organs in the female reproductive system help to sustain the female sex cells and secrete female hormones. It helps in the transportation of the cells to the site of fertilization and also lodges the fertilized egg cell on the wall of the uterus. It carries out a complicated process. The female reproductive system consists of the vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, external genital organs, and the uterus.
Ovaries are the primary reproductive organs. There are two gonads or ovaries. Each one is solid and has an ovoid shape. They are located on each side of the uterus. Now, let us move on to the normal size of ovary and its functions.
Know About the Normal Size of Ovary:
An ovary is about 3.5 cm long, 2 cm wide and 1 cm thick. Each ovary is covered on the outside with germinal epithelium which provides support to it. Furthermore, the ovarian substance is segregated into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The cortex is dense and appears granular due to the presence of ovarian follicles. The follicles contain the oocyte, i.e. an immature egg cell. The medulla is the loose connective tissue that has blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve cells.
Are you wondering, how the egg cells are transported to the uterus? Hold your breath, as we will throw some light on that as well. At the upper corners, the fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. When an ovary produces an egg, it pops right into the fallopian tube. The ovary is also a part of the endocrine system. Moreover, it also produces hormones such as estrogen.
Ovarian Volume in Premenopausal Women:
You already know that the normal size of ovary is 3.5cm x 2cm x 1cm. However, It can vary by another 0.5 cm on the upper side. The ovary changes in size after menopause. You will find that the ovaries generally measure about 2.5cm x 1.5cm x 1cm. It may be less as well. The ovary undergoes various changes with age, along with a decrease in size. As you grow from 30 years to 70 years, the ovarian volume undergoes reduction. Moreover, the average ovarian volumes of 9.8, 5.8, and 3.0 cm3 were obtained for the menstruating, postmenopausal, and premenarchal groups, respectively. Some women suffer from PCOS. Moreover, there is a direct correlation between the volume and the presence of follicles.
Types of Cysts in an Ovary:
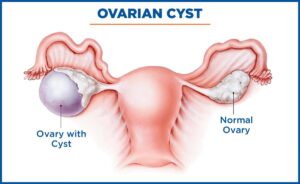
There may be cysts in the ovaries after a certain point in time. Wondering what cysts are? Furthermore, they are nothing but fluid-filled sacs. Mostly they are non-cancerous. The main causes behind them are endometriosis, hormonal imbalance, and pregnancy. The functional ovarian cyst is the most normal one. It is harmless. The various types of cysts include follicular cysts, endometriomas, corpus luteum cysts, hemorrhagic cysts, and simple cysts.
The size of an ovarian cyst is very important. It will determine if the condition requires surgery or not. Normally, doctors will not perform surgery unless and until the cysts are over 2-2.4 inches in size. Moreover, they also leave a simple cyst measuring about 10 cm alone. However, cancerous cysts need to be removed even if when they are small.
Functional cysts normally occur during monthly cycles. The follicular and corpus luteum are functional cysts. Most functional cysts are 2-5 cm in size, some might also be 8 cm. Ovulation generally takes place when these cysts are 2-3 cm in size.
Endometriomas (Cystic Lesions) occur during endometriosis. This condition points towards the growth of the cells of the uterus outside the wall. You will find doctors referring to them as chocolate cysts, due to a dark, brownish fluid within. They may be small, or large.
Ovary Size in PCOS:
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)is a term that is being discussed in medical circles today. It is quite common. The ovary size has a direct correlation to the blood flow in a woman with PCOS. You might also miss your monthly periods. This health condition affects every one in ten women. Such women generally suffer from hormonal imbalance and metabolism problems. It is the most common cause of infertility today. If you have PCOS, then maybe the ovary is not able to produce the egg as it should. Moreover, it may not be reduced in time, during the ovulation cycle. It also leads to cysts in the ovary.
PCOS can occur at any age after puberty. If you are obese, the risk magnifies. You must be aware of some of the symptoms of PCOS. The various symptoms that point towards the disease are:
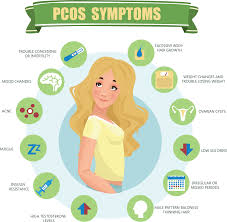
- Irregular menses – Such women may miss their periods, and also experience very light or a very heavy flow.
- Hirsutism is another symptom of PCOS – You will notice women with PCOS having a lot of unwanted hair on the body.
- Darkening of Skin – It is amongst the other visible effects. It is seen especially in the groin area, in armpits, and also under the breasts.
- Skin tags are another noticeable symptom of PCOS.
- Thinning hair might also be a symptom and should not be taken lightly.
PCOS in medical terms is a condition where each ovary secretes a large amount of the male hormone, called androgens. These excess hormones cause cysts and also cause the ovaries to swell up. In this condition, multiple follicles may appear as cysts. Ovaries are said to be polycystic when one or both have 12 or more follicles. They measure 2-9 mm.
Women diagnosed with PCOS are given Metformin. It can reduce the size of the ovary to a certain extent. Enlarged, polycystic appearing ovaries are a result of various ovarian cysts. The cysts grow and affect the size of the ovary. The cysts might not show any symptoms as well. Sometimes, the ovaries may enlarge in size or become twisted or dysfunctional.
Types of PCOS:
By now, you know that the size of ovaries is affected if you suffer from PCOS. There are four types of PCOS: Insulin-resistant PCOS, Inflammatory PCOS, Hidden-cause PCOS, and Birth pill-induced PCOS.
- Insulin-resistant type of PCOS – It is the most common type of PCOS and is generally caused by smoking, pollution, and a bad lifestyle. The high levels of insulin in the body prevent ovulation. It also leads to the creation of testosterone.
- Inflammatory type of PCOS – It is caused due to toxins, gluten in the body, and stress.
- Hidden-cause type of PCOS – Thyroid, Iodine deficiency, and zinc deficiency are a few of the reasons behind this PCOS. Artificial sweeteners can also lead to this type of PCOS.
- Birth pill-induced type of PCOS – It is the second-most common type of PCOS. It is a direct effect of taking contraceptives or birth-control pills. However, these effects do not last long. If you stop ingesting such pills, the effects are mostly reversed.
Ovarian Cyst Sizes:
Ovarian cysts vary in size from half an inch to four inches. It can be larger. If we go by cm, then cysts of 5cm are considered big, but those over 15cm are considered large, and those which reach the level of umbilicus are considered giant. For complex ovarian cysts, surgery is a must. Causes of an enlarged ovary may include a Corpus luteum cyst, a Dermoid cyst, a Follicle cyst, Endometrioma, or PCOS. These can also cause congenital abnormality, metastatic cancer, non-malignant tumour, or ovarian cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Ovarian Cysts:
Today, diagnosis is quite easy. Various technological advancements can help you detect it at an early stage. The diagnosis of cysts is mainly based on imaging. Ultrasonography is a gold standard in the medical fraternity today. Transvaginal Sonography is also very useful in diagnosing ovarian cysts.
If the ultrasound is inconclusive, then the next test that doctors prescribe is Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI. It is a very accurate process. Doctors even recommend blood tests that help to determine the severity of the cyst. Most cysts require proper medication and control. Very few require surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is very useful in removing small-sized cysts. Sometimes the cysts are drained.
You can also take precautions so that these don’t occur. Doctors generally suggest birth control pills if you have recurrent cysts. Birth control pills can reduce the risks of ovarian cancer. You can also prevent them through routine gynaecological examinations. Sometimes the symptoms of ovarian cancer and cysts may seem to be confusing. So it is better to explain the signs and symptoms to your doctor in detail. With some careful observation, you can prevent PCOS.
-by Abhrajita Mondal