Smallest Cell in Human Body
-by Abhrajita Mondal
–Reading Time – 7 min Approx
Do you want to know about the smallest cell in human body? Well, you definitely ought to know that. However, before you know that, you should know what cells are. If you go according to the definition, ‘cells are the building blocks of all living things’. The cells make up the human body. There are trillions of them. The cells give structure to the body too. Moreover, cells are responsible for converting food into energy. Cells carry out many special functions. They also contain genes. That is how we inherit the characteristics of our ancestors and forefathers.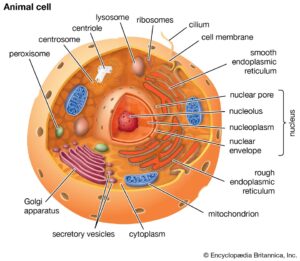
Cells have many different parts. Plants also have cells and so do animals. Cell organelles have specialized functions. You should know about the cell organelles and their functions. Otherwise, your knowledge will remain incomplete. The cytoplasm is the basic component of the cells. It is a jelly-like fluid that surrounds the nucleus.
The cell also has a cytoskeleton. Furthermore, it makes up the structural framework of the cells. It has several important functions. Moreover, it also controls the movement of the cell organelles. The other important cell organelles are the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, nucleus, plasma membrane and ribosomes.
Now, we come back to the smallest cell in human body. It is the Cerebellum’s Granule cell. It measures between 4 micrometers to 4.5 micrometers. However, there are certain arguments with regard to this concept. Many scientists say that the sperm cells in males are the smallest cells but there are differing opinions on this. As of now, we discuss about granule cells. The granule cells are found in the brain. They form a part of the cerebellar cortex. Moreover, they are a part of the smallest neurons in the brain. You will be amazed to know that there are about 50 billion of them. Apart from being the smallest, they are also the simplest. They are special cells that get inhibition through the Golgi cells.
The Smallest Cell in Human Body:
The Cerebellum’s Granule cell is the smallest cell in human body. The answer is out now. Excitation supposedly arises from these cells. To understand the function of these cells in a better manner, you ought to know about the morphology of the nervous system. So, let us get started. Everybody knows that the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of muscular activity. It also helps maintain posture and equilibrium. The cortex consists of deep folds. They are supported by the medulla. Now, you must know about the layers of the cortex. There is a molecular layer, ganglionic layer and granular layer.
Here, we are most concerned about the granular layer. It consists of the smallest granule cells. They have a dark-staining nuclei and minimal cytoplasm. They have only four or five dendrites that make contact with the mossy fibers. The contact point comprises the glomeruli. So, that is the reason why they are known to be the smallest cells in the body.
Somebody also asked, ‘Is RBC the smallest cell in human body’? Yes, they are small but not the smallest. RBCs have a diameter of 6 micrometers approximately. It may be less or more. These disc-shaped cells are an important part of the human body. Moreover, they are small enough to pass through the smallest blood vessels. They circulate inside the body for 120 days on average. After which, they are discarded through the spleen and liver. Therefore, you can call RBCs the second smallest cell in human body.
Longest Cell in Human Body:
After knowing about the smallest cell and the second smallest one in the human body, you might want to know more. So, the nerve cell or neuron is the longest cell in human body. They perform the task of relaying messages to the cells and tissues. Some neurons are almost 3 feet long. They also hold another title. They claim to be the longest living cells in the human body. Moreover, neurons remain the same over a long period of time.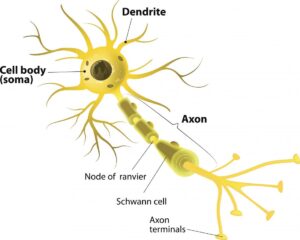
Do you want to know the structure of a neuron? Most of them have a cell body, an axon and dendrites. The cell consists of a nucleus and cytoplasm. The axon starts from the cell body and terminates at nerve endings. The dendrites receive messages or electrical impulses from other neurons. Synapses are the contact points between different neurons.
Neurons come in various shapes and sizes. In terms of function, there are three types of neurons. The sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. Sensory neurons help you to taste, smell, hear and see. Sensory neurons are triggered by chemical and physical stimuli.
Motor neurons help in voluntary and involuntary movements. These neurons allow the nervous system to communicate with the muscles, organs and glands present in the body. Interneurons are found inside the brain as well as the spinal cord. They are the most common ones. They form a complex circuit that helps you to react to external stimuli. In males, the largest cells are the neurons and more specifically the motor ones.
Largest Cell in Human Body:
Now, that you know that neurons are the largest cell in male human body, it is time to know about females. Which is the largest cell in the female body? It is the ovum. You can see it clearly with a naked eye. It is a reproductive cell. In females, the ovaries produce the ovum. In mammals, the ovum is fertilized inside the body to form a zygote. A zygote develops into a new organism after a gestation period. The human ovum measures 120 micrometers.
Do you want to know more about the ovum? Ooplasm is present inside the ovum. The nucleus is located in the centre along with the nucleoplasm. The ova of mammals contain a small portion of yolk for nourishment in the initial stages. However, birds like hens have enough yolk to last the entire incubation period.
The ovum carries the genetic information from the female. It also provides the initial nutrition to the embryo. After the required time has elapsed, the placenta takes over. If the eggs are not fertilized in the initial stages, the quality degrades. After fertilization, it undergoes cell division to give rise to a new life.
So, if you are asked to name the smallest and largest cell in human body, you can do that now.
Why do few Scientists call Sperms the Smallest Cell in the Human Body?
It is true that the Cerebellum’s Granule Cell is the smallest cell. However, few scientists have suggested that the sperm is the smallest by volume. The sperm cell heads measure 4 micrometers in length. Moreover, the sperm is very complex in nature. The volume is 85,000 times less than that of an Ovum.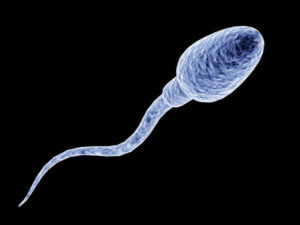
You should know about the structure of the sperm in more detail. The mature sperm cell is only 0.05 mm long. It has a head, body and tail. The mitochondria, which is the energy storehouse comprises the connecting part of the head and body. The protein fibers make up the tail. The sperms swim around in with the help of the tail. You need to understand that they are fragile. If the temperature inside the testes is high, they can die. That is the reason, the scrotal sacs have a thermostat that keep sperms alive at optimum temperature.
Sperms compete against one another when they are reaching the egg. Some swim fast and others slow. The fastest swimmer reaches the egg first and fertilizes it. The male semen or seminal fluid has sperms in it along with other nutrients. A man in one lifetime produces around 12 trillion sperms. That is quite a number, isn’t it?
Now, you have a fair idea about the smallest, second smallest, longest and largest cells in human body. Humans are truly a complex creation. Each cell inside the human body has its own structure and function. There are about 200 different cell varieties in the human body. Each one needs to perform a specific function without which humans cannot function.
Today, you have come to know about a few cells like RBCs, neurons, granule cells, sperm cells, ovum or egg cells. Well, there are many more. Any average human being has 30 trillion cells inside the body. The RBCs are a huge majority. Apart from human body cells, there are bacterial cells as well. Scientists are continuously evaluating the structure and function of the various cells in the human body. So, you should not be surprised if you hear about more such cells in the future.
-by Abhrajita Mondal
Dear Reader, Hope you liked the post. If you think our initiative “The Creative Post” is worth supporting, then please support us by paying the amount you think we are worthy of. We believe, the value of content should be decided by the consumer. Hence we request you to evaluate our worth and pay accordingly by Clicking Here.