Who Gave The Cell Theory?
-by Abhrajita Mondal
–Reading Time – 7 min Approx
–Edited by – Srishti Bhattacharyya
The cell theory states the postulates of the basic cells that make up all living beings. It says that all living organisms are made of cells. The Cell Theory forms the foundation of biology. Now, you must be wondering who gave the cell theory? In 1839, German botanist Matthias Schleiden and an English zoologist Theodor Schwann explained the foundation of the basic tenets of modern biology. However, the initial discovery can be attributed to Robert Hooke. These eminent scientists concluded that:
- The cell is the basic structure of all living organisms.
- Cells retain a dual existence, as a separate identity and also as a building block.
- Cells are formed by free-cell formation. It is very similar to the formation of crystals.
These are the 3 parts of the cell theory. This theory was universally accepted. However, later some biologists came across non-cellular entities. Today, we know them as viruses. Thus, it disagrees with the first tenet of the cell theory.
With the advancement in technology, more complex microscopes were being used in laboratories. The ones used in the 1600s by Antony van Leeuwenhoek were simple and less efficient. Although the lenses were not as powerful, still the scientist managed to discover bacteria and protozoa. With the advancement in lenses, microscope construction, and staining techniques, scientists discovered more elements within the cells. In fact, Robert Hooke penned down the term ‘cell’ for box-like structures in cork. Still, Schleiden and Schwann are credited for the development of the theory.
Who Gave the Cell Theory?
Many others were involved in the discovery. You ought to know who gave the cell theory in detail. Here, in 1665, details of around 60 objects were seen under a compound microscope. Initially, Robert Hooke was not aware of any terminology but later coined his own. The honeycomb-like structure appealed to him a lot. Initially, he could only see a color or stain. However, Antony van Leeuwenhoek took up from there. He made use of improved lenses that could magnify objects 300 fold, or 270 times. You ought to know about the Modern Cell Theory as well. In 1839, Schleiden said, that cells were made by a crystallization process.
The classical cell theory gave way to the Modern Cell Theory. However, the crystallization process was rejected in the modern version. All living beings are supposedly made up of one or more cells. Cell division gives rise to more cells and in this way, energy flow occurs from one cell to another. In addition to the above postulates, the theory has a few additions. Firstly, the DNA passes from one cell to another during cell division. Secondly, the modern cell theory states that cells of organisms in a similar species are alike. Moreover, they are alike structurally and chemically. Thirdly, energy flows between cells. You should know about the five scientists who contributed to the Cell Theory –
Robert Hooke is the first scientist who contributed to the cell theory. It was way back in 1665 when he discovered cells in a cork. He made the observation under a self-made microscope and published his findings in ‘Micrographia’. This is how the classical cell theory was developed.
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek saw bacteria, sperms, and some free-living pond cells for the very first time.
J.E. Purkenjee discovered protoplasm.
Robert Browen discovered the nucleus.
The scientist duo Schleiden and Schwann are the original contributors to the cell theory. It is known as Classical Cell Theory.
Rudolf Virchow stated ‘omnis cellula-e-cellula.’ It means that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Opposing Concepts of the Cell Theory:
In the cell theory, the internal contents were termed as ‘protoplasm’. It is a jelly-like substance. The idea of the membrane also came into being. Osmosis was brought forward in the year 1827. However, it was not until 1877 that Botanist Pfeffer proposed the Membrane Theory of Cell Physiology. In this view, the cell membrane gained a lot of importance. More scientists started studying the solutes present inside the cell and their permeability. Osmosis, permeability, and electrical qualities of the cells gained more importance. Some quarters believed that the electrical qualities of the cell were due to the cell membrane. While others believed it to be due to the protoplasm inside. The theories that preceded the studies are Membrane theory and Mosaic theory.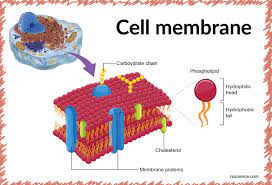
The Membrane Theory concentrates on the features of the cell membrane. It is considered to be semi-permeable in nature. It is supposedly permeable to solvents and impermeable to solutes. It gave rise to the term Osmosis. According to the Membrane Theory, the primary function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell and its contents. It consists of a phospholipid layer with proteins embedded into it. Plasma membranes are also flexible. They selectively allow the red blood cells and white blood cells to pass through. It also plays a major role in anchoring the cytoskeleton and maintains the cell potential. One of the more complex functions of the membrane is the transmission of complex proteins.
Moreover, the Fluid-Mosaic Model proposed by S. J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson describes the plasma membrane in a detailed manner. It is supposed to be made up of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The mosaic pattern gives the membrane a fluid nature. The main components are phospholipids. Proteins are the second-most important component. According to scientists, there are several reasons behind the fluidity of the membrane. Firstly, it is the mosaic nature, it can allow solvents and solutes to pass in and out. You can compare it with a needle. The nature of the phospholipids also gives the cell membrane its fluid structure. In animals, there is a third component responsible for fluidity. It is the cholesterol layer.
Plant Cells and Animal Cells:
All the vital activities within the plant and animal bodies are performed by the cells. Moreover, you must classify organisms based on the number of cells. In the environment, plants are generally referred to as the producers whereas animals are referred to as the consumers. Therefore, their constitution and cell structure also vary. You will know about that in detail. These are under the findings of the Modern Cell Theory and further studies.
Moreover, the organisms are classified based on the number of cells they carry. Unicellular organisms are single-celled whereas, multicellular organisms have many cells. Now, let us go back to plant and animal cells. There is a lot of difference between their structure and function. Additionally, there are organelles inside the cells and each organelle has a function to carry out. Some cell organelles are common to both plants and animals. Most higher organisms have eukaryotic cells. A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and ribosomes, to name a few. Both plants and animal cells are eukaryotic. They are said to function similarly. However, there are some strong differences between both.
You should know about the plant cells first. Plant cells are square or rectangular in shape. They have a cell, cell membrane, and reticulum. You will also come across the bead-like nucleus in a corner of the cell. Lysosomes are rarely present in the plant cells and centrosomes are totally absent. Plant cells contain Golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, plastids, single vacuole, and very few mitochondria. They are autotrophic. Now, let us move on to the animal cells. They are mostly irregular in shape and do not have a cell wall. However, they do have a cell membrane and endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleus is present and lies in the center of the cell. Lysosomes, centrosomes, Golgi apparatus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and multiple vacuoles are present. Cilia is a constant feature of most animal cells. Animal cells contain a large number of mitochondria and follow the heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
Cell Structure in Details:
You should know about some of the important structures of the cell in more detail. We have spent a considerable amount of time on the cell membrane. What about the other parts? They have an important role to play too along with the membrane. The Nucleus is the cell control center. It contains DNA information and determines the cell’s functioning. The cytoplasm is another important component that needs to be given credit for cell functioning. It helps the organelles function properly.
Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cells. Moreover, the Endoplasmic Reticulum forms the skeletal structure of the cell. Golgi bodies help in secretion and intracellular transport. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell. It helps in cellular respiration and generates ATPs.
Now, that you know about the origins of the cell and its various components, you can understand how cellular processes take place. It is important for a foundational knowledge of the basis of life on earth.
-by Abhrajita Mondal
Dear Reader, Hope you liked the post. If you think our initiative “The Creative Post” is worth supporting, then please support us by paying the amount you think we are worthy of. We believe, the value of content should be decided by the consumer. Hence we request you to evaluate our worth and pay accordingly by Clicking Here.