(Reading Time: 20 min Approx)
2020 is on! After Marty (back to the Future II) has returned home post a trip to the future (2015), we have moved five years ahead. Let’s talk some High-Tech Futuristic Stuff then. If you are a ‘Tech Savvy’ and want to know how ‘New’ this year is going to be; then my friend you’ve come to the right place. Like new trends in fashion & lifestyle; technology is also in hype. The future is no longer far away because you are already living it.
Here are the ventures in the field of technology that are soon to hug you this 2020.
- Li-Fi:
Li-Fi is high speed bi-directional networked and mobile communication of data using light. Li-Fi comprises of multiple light bulbs that form a wireless network, offering a substantially similar user experience to Wi-Fi except using the light spectrum.
The way Li-Fi works is simple but powerful. When a constant current is applied to an LED light bulb, a constant stream of photons is emitted from the bulb which is seen as illumination. LED bulbs are semiconductor devices, which means the current, and therefore the illumination can be modulated at extremely high speeds which can be detected by the photo detector. Using this technique allows for high-speed information can be transmitted from an LED light bulb.
Radio frequency communication requires radio circuits, antennas and complex receivers, whereas Li-Fi is much simpler and uses direct modulation methods like those used in low-cost infrared communications devices such as remote-control units. LED light bulbs have high intensities and therefore can achieve very large data rates.
For example, there is an average Wi-Fi router in an office that provides 100 Mbps and 15 employees are connected to it. It means you might only be able to access 4 Mbps. However, with a Li-Fi network complies that offer 42 Mbps per light bulb; even if you have only 8 lights in your room those same 15 people can share 300 Mbps.
Today there are real life applications and benefits for implementing Li-Fi. It can enable secure wireless communications, connectivity in RF hostile environments such as petrochemical plants and hospitals. Li-Fi also provides high speed, dense and reliable networks for enterprise environments and a pathway to enable smart buildings, transport, cities, and nations.
- 5G:
In 2019, the wireless industry began shifting to 5G, a technology that can deliver data at such incredibly fast speeds that people will be able to download entire movies in a few seconds. Yet the roll out of 5G was anticlimactic and uneven. Across the United States, carriers deployed 5G in just a few dozen cities. And only a handful of new smartphones last year worked with the new cellular technology.

In 2020, 5G will gain some momentum. Verizon said it expected half the nation to have access to 5G this year. AT&T, which offers two types of 5G — 5G Evolution, which is incrementally faster than 4G, and 5G Plus, which is the ultrafast version — said it expected 5G Plus to reach parts of 30 cities by early 2020.
Another sign that 5G is really taking hold? A broader set of devices will support the new wireless standard. Samsung, for one, has begun including 5G support on some of its newer Galaxy devices. Apple, which declined to comment, is also expected to release its first 5G-compatible iPhones this year.
- Self-driving Cars:
Electrification, autonomous driving and connectivity are the three factors that will shape the future of the car, that is to say the autonomous and connected electric car.
The electrification of cars will solve the problem of pollution and noise of current cars. Autonomous driving will greatly reduce the number of accidents. The connectivity will allow passengers to consult information (weather, road traffic, etc.) and to take care during the journey.

Before continuing, I will define what an autonomous car is. An autonomous car (driver-less car or self-driving car) is a vehicle capable of driving on the road without the intervention of a driver. It is a vehicle that is equipped with many sensors like ultrasonic sensors, cameras in order to perceive its environment. The data collected by the sensors are processed by software and processors to make the data fusion in order to observe its environment and to detect other vehicles, obstacles, signs and pavement limits. Then artificial intelligence algorithms will decide the action to be performed on the vehicle controls (steering wheel, accelerator, brake, etc.).
Driver less cars will also be connected and will have an internet connection. They will be able to inform the user and his passengers, the weather, road traffic and the formation of a traffic jam. They will also give passengers time, which will be an opportunity for Google and Apple to introduce embedded services like infotainment in self-driving cars.
- Blockchain:
The blockchain is a technology for storing and transmitting information, transparent, secure, decentralized, and operating without a central organ. In short, it is a kind of digital data management protocol, a large secure and transparent database. The blockchain can be seen as a kind of account book or register that contains a list of all exchanges made between users.
The blockchain is often wrongly confused with Bitcoin, but Bitcoin is a Cryptocurrency that uses the Blockchain to ensure trace-ability of transactions since each bitcoin has its own encryption code. Thus, a user can only use his bitcoins with a single recipient corresponding to a single transaction.
According to a Microsoft show conference on the blockchain, it turns out that the blockchain can be used in three distinct categories:
The transfer of assets: currency, securities, shares, bonds, votes, etc.
Register: better trace-ability of products and assets.
Smart contracts: autonomous programs that automatically execute the terms and conditions of a contract, without requiring human intervention once started.
This blockchain technology could thus find many concrete applications such as:
An online voting system: For example, during an internal election, the use of the blockchain allows a secure vote and a transparent result with a quick announcement of the results. The blockchain applied to the online voting system thus avoids any fraud and contesting voting results and could therefore interest political parties or countries that sometimes have difficulty counting votes and fraud problems.
Automatic compensation in the event of late or cancelled flights: For example, travel insurance schemes may use the principle of smart contracts which are based on autonomous programs which automatically launch the conditions of the contract, without the person must fill in any form.
A money transfer platform: The advantages of using the blockchain in this type of platform are the speed of transfers (a few minutes against several days for some transfers abroad) and the low cost of these transfers (a few cents for each transaction) through Cryptocurrencies that are convertible into traditional currencies.
The blockchain can therefore have many applications in various sectors such as banking, insurance, real estate, health, energy, transport, online voting, and thus finds other applications other than the monetary field.
- The 3D printing revolution:
In recent years, 3D printing has become possible thanks to 3D printers. 3D printers follow the same principle as 2D printers, but instead of printing ink on sheets of paper, the 3D printer prints objects by superimposing thin layers of materials such as plastic, clay, resin and others. From a 3D software or a 3D scanner, it is possible to model objects and then print them with the 3D printer. The printing possibilities are immense with the 3D printer, it is practically possible to print all possible forms. The only constraints are the size of the printer and the imagination of the user.

The 3D printer can be used in many fields of applications such as industry, robotics, jewellery, medicine, food, fashion, armament, DIY, architecture, design, health, aeronautics and marketing. There are even 3D nano printers, such as nano scribe, which prints on a scale of a few microns. Based on a CAD model of a spacecraft, the 3D nano printer, nano scribe, prints using lasers and rotating mirrors to direct the beams in order to create a multi-layer structure by polymerization.
Some 3D printers can print objects of several meters. This allows, for example, to print some pieces of wood to assemble a house. The project ‘WikiHouse’, is an open-source project that offers models of home to assemble oneself from models printed in 3D. These homes can especially be an opportunity to shelter millions of homeless people.
In Amsterdam, architects use the 3D printer to print their models but also to print their homes directly. In Shanghai, based on the assumption that cars and planes are mass-produced, an entrepreneur thought to do the same thing with the houses and therefore created a company that manufactures series houses with 3D printers by mixing concrete with a other material to solidify the house. One can also imagine that furniture can also be printed from 3D models.
To conclude on 3D printing, 3D printers are a real technological revolution because they will allow companies to create their products quickly and accurately and also to individuals to build their own objects and perhaps become architects of their own homes.
- World’s smallest computer:
The Smallest Computer in the World Fits on a Grain of Rice. Researchers at the University of Michigan just created the world’s smallest computer (again). Their previous micro-computer, the Michigan Micro Mote, measured 2x2x4mm. It was a complete, functioning system powered by solar cell batteries. But in March this year, IBM announced a new, smaller computer, which measured 1×1 mm, and was smaller than a grain of salt. It “raised a few eyebrows at the University of Michigan.”
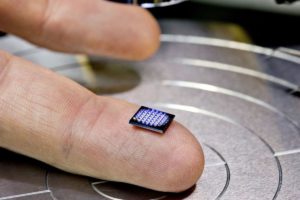
After all, it’s unclear if the IBM computer even count as an actual microcomputer. The IBM device lost all its programming and data as soon as it turns off, unlike the Michigan Micro Mote, which retained its programming even when it wasn’t externally powered. “It’s more of a matter of opinion whether they have the minimum functionality required,” said David Blaauw, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at University of Michigan who helped develop the University of Michigan’s newest tiny device. If the IBM machine constituted a computer, then University of Michigan would work to gain back their title: their latest micro device measures 0.3 mm per side (1/10th the size of IBM’s computer) and is smaller than a grain of rice.
The device was designed to be a precision temperature sensor that can report temperatures in clusters of cells with an error of about 0.1 degrees Celsius. “When we first made our millimeter system, we actually didn’t know exactly all the things it would be useful for. But once we published it, we started receiving dozens and dozens and dozens of inquiries,” Blaauw said. It could, for instance, measure the temperature of tumors and conduct other cancer studies, monitor oil reservoirs, conduct audio or visual surveillance, or help in “tiny snail studies.”
Here are some upcoming ventures that will be in your daily life soon. Let’s have a quick glance-
- Smart mirrors that check your health:
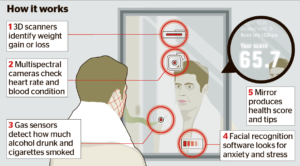
A quick glance in the mirror each morning gives you a visual cue on how you’re feeling and looking to the outside world. Now imagine a future where smart mirrors could scan you and tell you about potential health problems, vitamin deficiencies or warnings signs of underlying issues. Pre-emptive information about these symptoms might help you prepare.
- 3D printed food:

We’re not quite in a world where Star Trek replicators exist, and we can magic up anything we want out of thin air. But 3D printing technology is coming along quickly, and companies are already experimenting with printing food. Fridge running a bit low? Not a problem for future you, just print some cakes, vegetables or even a pizza. We’re dreaming big here.
3D printing is taking off in other areas too. From creating Aeroplane and vehicle parts, replacement joints such as hips, or pieces for a board game, it still has huge potential to change our lives in the coming years. The materials being used to print with are evolving too, and now include Graphene that is “lighter than air” but 10 times stronger than steel.
- Lab-grown meats:
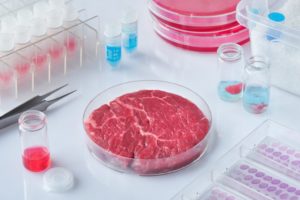
Cows on tower blocks might seem a bit bonkers, but lab-grown meat is a real thing that’s already being worked on. If scientists can develop a cost-effective way to grow edible meat in the lab it would change the way, we live and eat forever.
This change not only cuts down the ecological damage meat farming does to the world, but also makes for an ethical alternative to meat eating that many people could enjoy.
- High-rise farms:

As the population of Earth continues to grow, living space also shrinks, not only for human beings but for the animals and plants we rely on too. It’s reasonable to see a future where tech will need to be developed to allow for farmland in unusual places. This concept of high-rise farms in the middle of a city isn’t totally out of this world.
- Space tourism:

We can fly to virtually any country in the world without any trouble, but what if we could all one day see the earth from space?
Companies such as Virgin Galactic, SpaceX and even Amazon’s Blue Origin, want to make it a reality one day, and give us a (very expensive) seat aboard a spaceship to take us into orbit. Passengers on Amazon’s New Shepard space shuttle will be taken 100km above sea level, before parachuting back to earth.
- Wearable screens:

We might be currently daydreaming of fold-able phones and screens, but the future might well be screen less. There are already plenty of touch-capable projector-like devices that can beam usable screens onto your skin, clothing or other surfaces. The future of smartphone tech might not even require a device in your pocket but something you wear or have implanted.
- Fridges that order for you:

If 3D printed food seems unrealistic, how about a refrigerator that senses when you’re running low on something and orders it for you? This tech already exists and is getting better and better every year.
Eventually, it’ll be so common every home will have one and you’ll never need to pop out to the supermarket again.
- Smart toothbrushes that send data to your dentist:

We already have intelligent toothbrushes which keep an eye on your brushing technique to make sure you’re doing a good thorough job each time you brush.
But what if your toothbrush could send that data to your dentist so they don’t even need to ask if you’re flossing daily? Or, perhaps less terrifyingly, using sensors to monitor your dental health by scanning for cavities or plaque build-up.
So, buckle up folks. The future of technological revolution is here now.


What are some of the high-tech futuristic trends and advancements that we can expect to see in the year 2020, especially for those who are tech-savvy and interested in staying updated with the latest technological developments?